Configuring Black Duck
Black Duck is a software composition analysis (SCA) tool that detects security vulnerabilities in third-party components of a software project.
It is possible to incorporate Black Duck results in TICS.
Prerequisites
For a successful Black Duck integration, the following prerequisites
must be met:
- The results must be available in the Black Duck server dashboard. TICS only retrieves the results and does not perform the analysis.
- The Black Duck properties have to be configured correctly, see below.
- The Black Duck authentication token has to be configured correctly, see below.
- The Black Duck data fetcher,
bdfetcher, has to be configured correctly, see below. - The Black Duck rulesets have to be configured correctly, see below.
Basic configuration
To use Black Duck, one has to set up the required properties in either the global configuration file SERVER.yaml or in the project-specific configuration file PROJECTS.yaml. Black Duck properties configured globally in SERVER.yaml will apply to all projects. If the properties are declared both on the SERVER level, i.e. in SERVER.yaml, and also on the PROJECT level, i.e. PROJECTS.yaml, the project-specific properties will overwrite the global properties. If they are declared in the PROJECT level, they can be declared either inside or outside a branch name (inside VIEWS) of a project.
Syntax
The following properties can be declared either on the SERVER level or on the PROJECT level. Of these properties, it is mandatory to have the URL configured.
TOOLS:
BlackDuck:
WEBSERVICE:
URL: URL of a Black Duck server, for example: https://blackduck.tiobe.com
[AUTHENTICATIONKEYFILE: a relative path of a file containing a Black Duck authentication token.
The path is relative to the default folder of the TICS configuration directory, i.e. ticsfs/cfg/default]
[PAGESIZE: Page size for Black Duck API calls. Value should be between 1 and 1000.
If set outside this range, or not configured, the Black Duck data fetcher will use the value 1000.]
[TIMEOUT: The time a webservice call may take (in seconds) before it is aborted. Value should be larger than 0.
If set outside this range, or not configured, the Black Duck data fetcher will use the value 1800.]
[NR_OF_RETRIES: The number retries when the data cannot be fetched because of connection timeout. Value should be larger than 0.
If set outside this range, or not configured, the Black Duck data fetcher will use the value 5.]
[RETRY_INTERVAL: The time (in seconds) between retries. Value should be larger than 0.
If set outside this range, or not configured, the Black Duck data fetcher will use the value 3.]
[HOSTNAMEVERIFICATION: Enable or disable host name verification of the Black Duck server. Can be set with values
'true', '1', 'false' or '0'. If configured, will be used to set (or override) the value of
environment variable TICSHOSTNAMEVERIFICATION. If TICSHOSTNAMEVERIFICATION is not configured, the Black Duck fetcher will enable the
host name verification by default.]
[TRUSTSTRATEGY: Set the strategy to establish trustworthiness of certificates of the Black Duck Server. Can be set with
relevant values such as 'all' or 'self-signed'. If configured, will be used to set (or override) the value of
environment variable TICSTRUSTSTRATEGY. If TICSTRUSTSTRATEGY is not configured, the Black Duck fetcher will use the self-signed
trust strategy by default.]
The DATASOURCES property and its sub-properties are mandatory and have to be applied on the PROJECT level, either inside or outside a branch name, as shown in the following examples:
project name:
TOOLS:
BlackDuck:
DATASOURCES : [
[
PROJECT: Project name in the Black Duck server
VERSIONS: [Project versions in the Black Duck server],
]+
]
project name:
VIEWS:
branch name:
TOOLS:
BlackDuck:
DATASOURCES : [
[
PROJECT: Project name in the Black Duck server
VERSIONS: [Project versions in the Black Duck server],
]+
]
Examples for DATASOURCES and other properties:
TICS needs the Black Duck project/version names to be configured to fetch results.
Note that at the moment TICS will only allow a data source from one project and one project version.
If multiple projects and/or multiple versions are configured, only the first project and the first version will be used. The rest will be ignored.
The configuration of DATASOURCES, as well as other properties, are shown in the following examples:
cpp-game-project:
TOOLS:
BlackDuck:
DATASOURCES:
- PROJECT: blackduck-demo-cpp
VERSIONS:
- NAME: 1.0.0
WEBSERVICE:
URL: https://blackduck.tiobe.com
AUTHENTICATIONKEYFILE: ../common/blackduck-auth-key.yaml
PAGESIZE: 500
TIMEOUT: 5
NR_OF_RETRIES: 10
RETRY_INTERVAL: 2
cpp-game-project:
VIEWS:
master:
TOOLS:
BlackDuck:
WEBSERVICE:
URL: https://blackduck.tiobe.com
AUTHENTICATIONKEYFILE: blackduck-auth-key.yaml
PAGESIZE: 400
TIMEOUT: 10
NR_OF_RETRIES: 3
RETRY_INTERVAL: 4
DATASOURCES:
- PROJECT: blackduck-demo-cpp
VERSIONS:
- NAME: 4.0.0
Authentication Token
An authentication token is required to fetch data from the Black Duck server.
This token is used for authenticating API calls from TICS to the BlackDuck server.
An authentication token can be generated from the Black Duck server dashboard in the 'My Access Tokens' menu.
There are two ways to provide this authentication token to TICS:
- Adding a yaml-formatted authentication key file in the TICS configuration directory.
- Configuring an authentication token in the environment variable
TICS_BD_AUTHTOKEN.
Configuring an authentication key file
One way to configure the Black Duck authentication token is to add a yaml-formatted
authentication key file in the TICS configuration directory.
This authentication key file should contain the field token followed by an authentication token value
as shown in the example below:
token: TokenFromAuthFileC00MjlkLTg2MWItMmM1NDE0MmU2N2IyOmM5YWEyMzdhLTEwMGYtNDM2My04OTJkLTliYWUyMGFjY1234567
Once the authentication key file has been added in the TICS configuration directory, configure the
AUTHENTICATIONKEYFILE property for Black Duck.
Assign a relative path of the authentication key file to the property
as shown in the example below:
TOOLS:
BlackDuck:
WEBSERVICE:
URL: https://blackduck.tiobe.com
AUTHENTICATIONKEYFILE: ../common/blackduck-auth-key.yaml
Configuring a TICS_BD_AUTHTOKEN environment variable
Alternatively, the BlackDuck authentication token can be set up in the environment variable
TICS_BD_AUTHTOKEN as shown in the example below.
C:\Users\Public>set TICS_BD_AUTHTOKEN TICS_BD_AUTHTOKEN=PresetTokenInEnvVarMzllLTg5MTItMDYxNzk2ZTMwMzJhOjljZWM1Yzg5LWM1NGUtNDc0Ny1hZWU3LWY5Y2QyZDNhN1234567
If both the AUTHENTICATIONKEYFILE property and the environment variable
TICS_BD_AUTHTOKEN are configured, TICS will use the authentication token
configured in the AUTHENTICATIONKEYFILE property.
Black Duck Rulesets
Black Duck rulesets should be configured in SERVER.yaml for metric SECURITY of each relevant language. Black Duck rulesets
are prefixed with 'BLACKDUCK_' as shown in the examples below:
C:
RULESETS:
- METRIC: SECURITY
RULESDIR: 4.0/security/BLACKDUCK_C
NAME: BlackDuck C Security
CPP:
RULESETS:
- METRIC: SECURITY
RULESDIR: 4.0/security/BLACKDUCK_CPP
NAME: BlackDuck CPP Security
Black Duck Fetcher
TICS uses a Black Duck fetcher, an executable java artifact called bdfetcher that fetches data from the Black Duck server.
To use Black Duck properly in TICS, bdfetcher needs to be specified as one of the checkers in the checkers
property of config.yaml as shown below.
versions:
checkers:
bdfetcher:
version: 1.0.0
The latest version of bdfetcher can be found on our download site inside the codecheckers/bdfetcher folder.
Black Duck Custom Fields
Black Duck custom fields are system-wide properties in a Black Duck dashboard that can help a user organize large projects and manage open source components. With custom fields, a user can create properties that are important for the company to track, and (s)he can apply those properties to particular projects and components (Black Duck: Custom Fields).
TICS supports two Black Duck custom fields, i.e. the Language custom field and the Scope custom field. We discuss each custom field in the following subsections.
Black Duck Language custom field
When language information of a software component is lacking in Black Duck, TICS applies the component's violations to all files of all languages. This makes it harder to pinpoint where the issue lies. It also results in too many not applicable violations. Therefore, a user should be able to associate Black Duck violations with (a) specific language(s), even when the language for a component in Black Duck is missing, so the user can better identify which violations actually apply to her/his language. In case Black Duck provides the wrong language, the user should be able to override this by specifying the correct language.
This is done by using an optional component-level custom field called Language.
Creating the Language custom field in a Black Duck dashboard
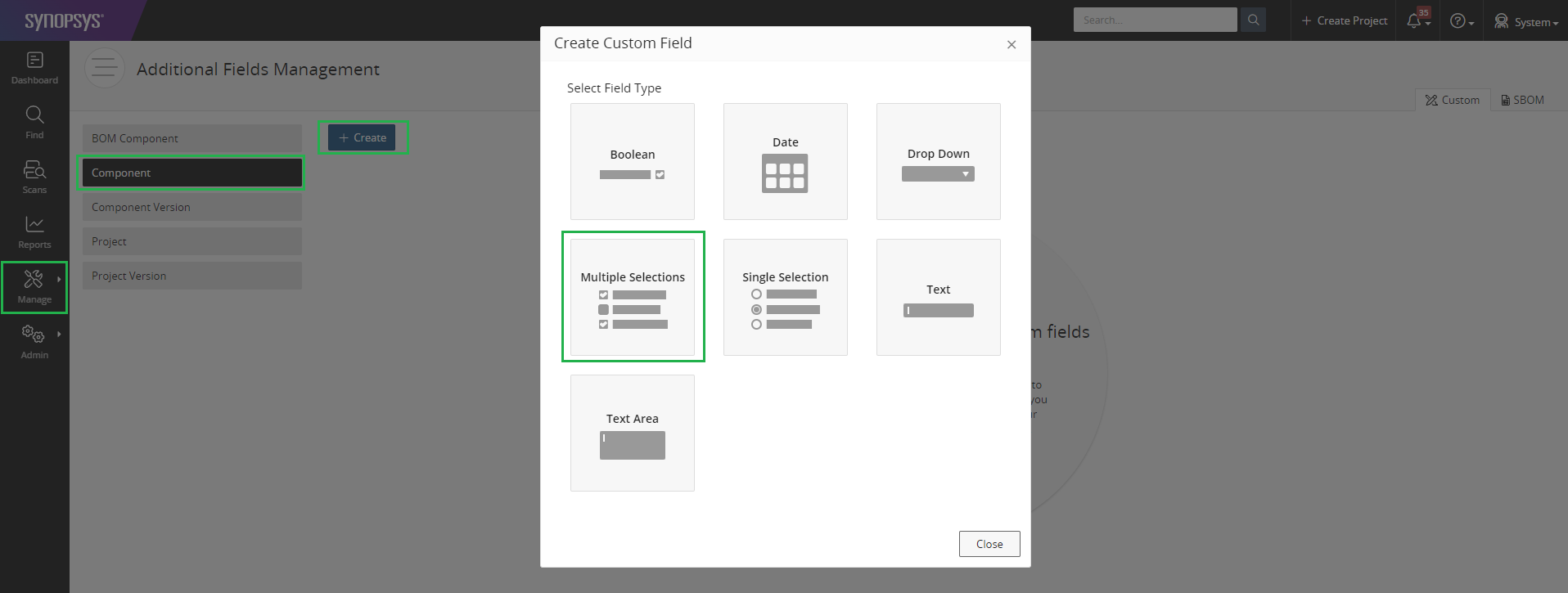
The Language custom field is applied on a generic component. To create the custom field, from a Black Duck dashboard, go to menu Manage -> Custom -> Component.
Click on the + Create button, choose Multiple Selections field type, as
shown below.
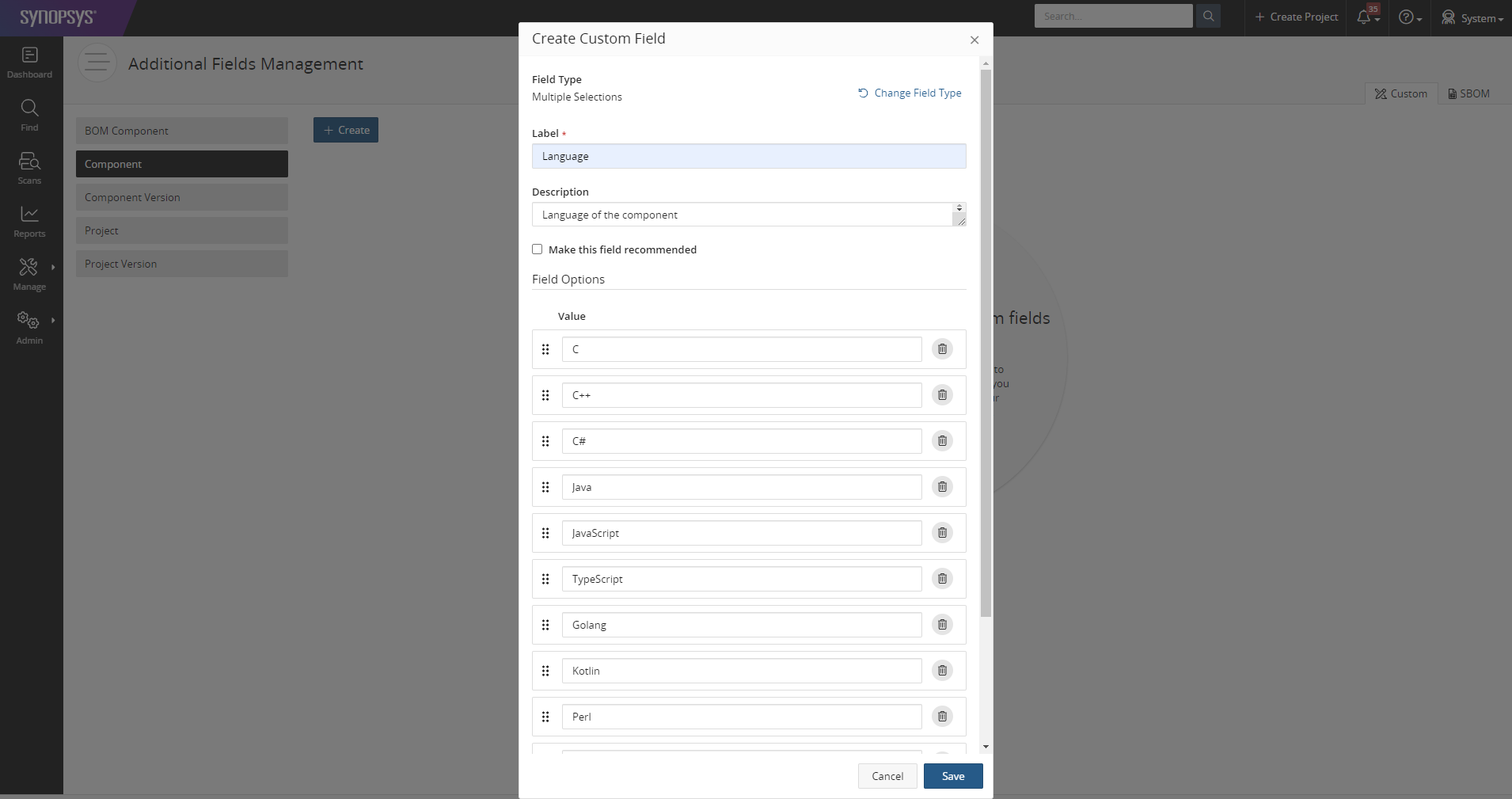
Fill out the relevant fields for the custom field as described below.
- Set the
Labelof the custom field to "Language". - Set the
Descriptionof the custom field to "Language of the component". - Propagate the
Field Optionswith languages that are supported by Black Duck. Please use the following values so that the Black Duck fetcher can correctly propagate them to TICS: C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, TypeScript, Golang, Kotlin, Perl, Python, Scala, Swift, Lua, SQL, Dart, Visual Basic and XAML.
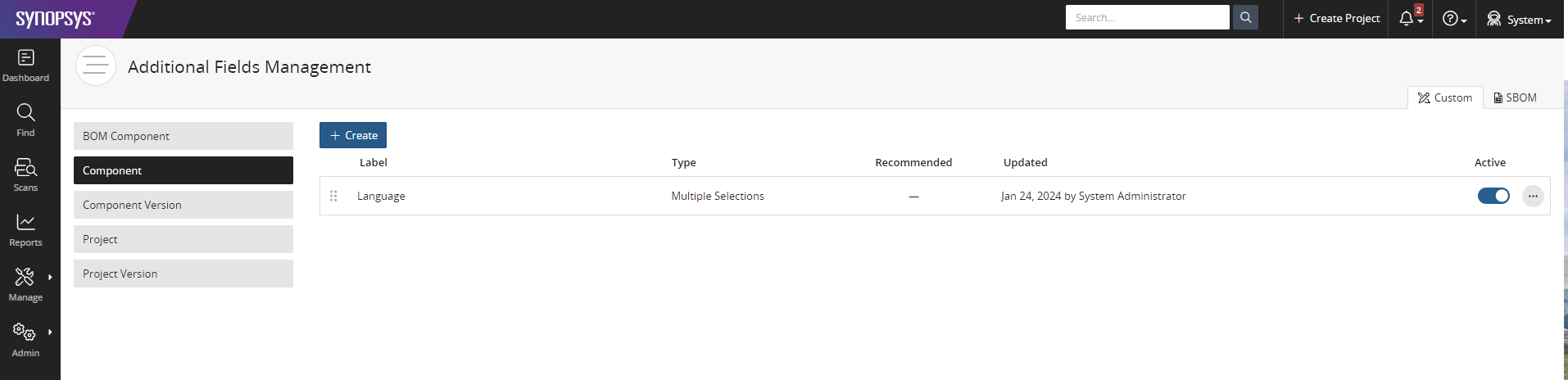
Click the Save button and activate the Language custom field by sliding the Active option slider for the custom field.
Setting the Language custom field in a Black Duck dashboard
Now that we have created a generic-component-level Language custom field, we can set a value for this custom field.
First, open a page of a generic component which may or may not have a built-in language information.
In the example below, we open the page of component
"ethereum/aleth" which has unknown built-in language.
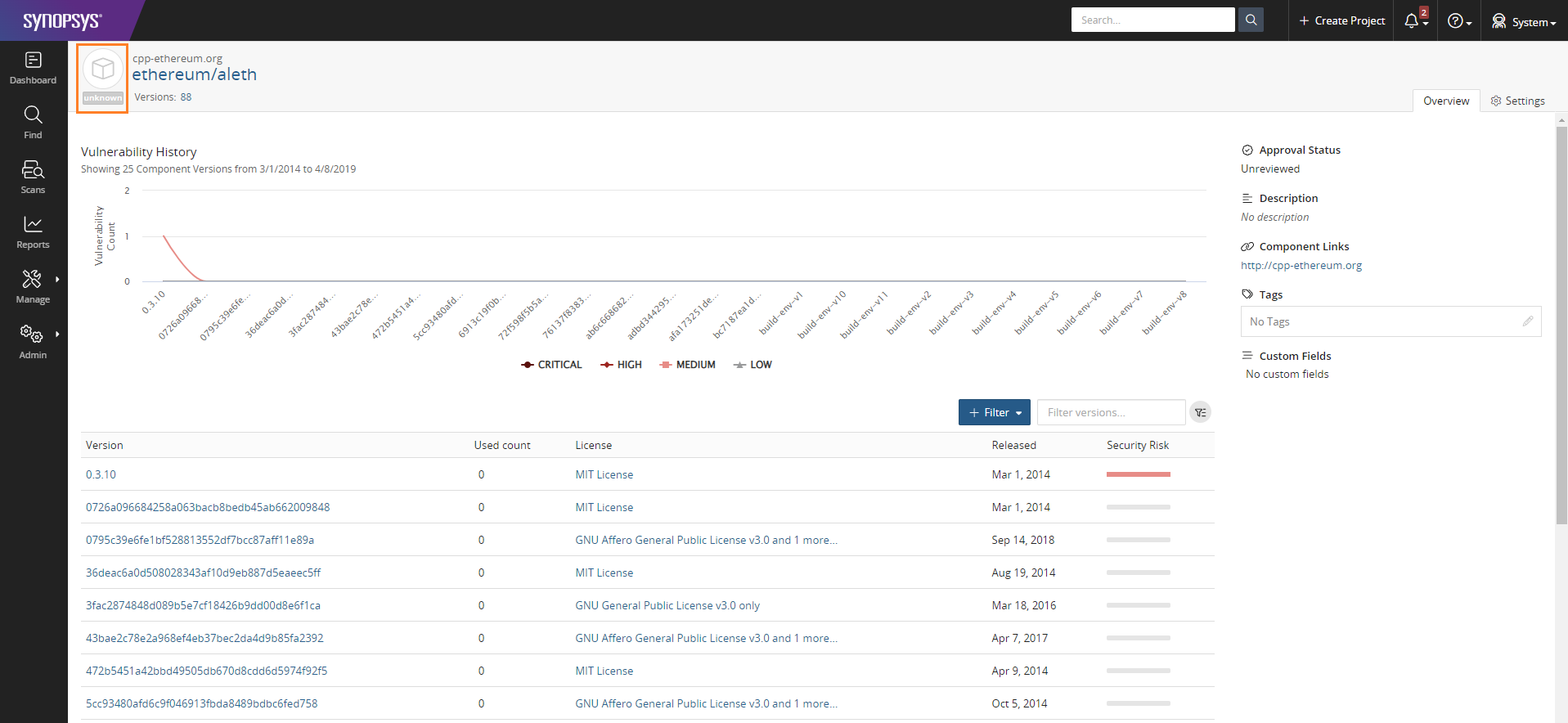
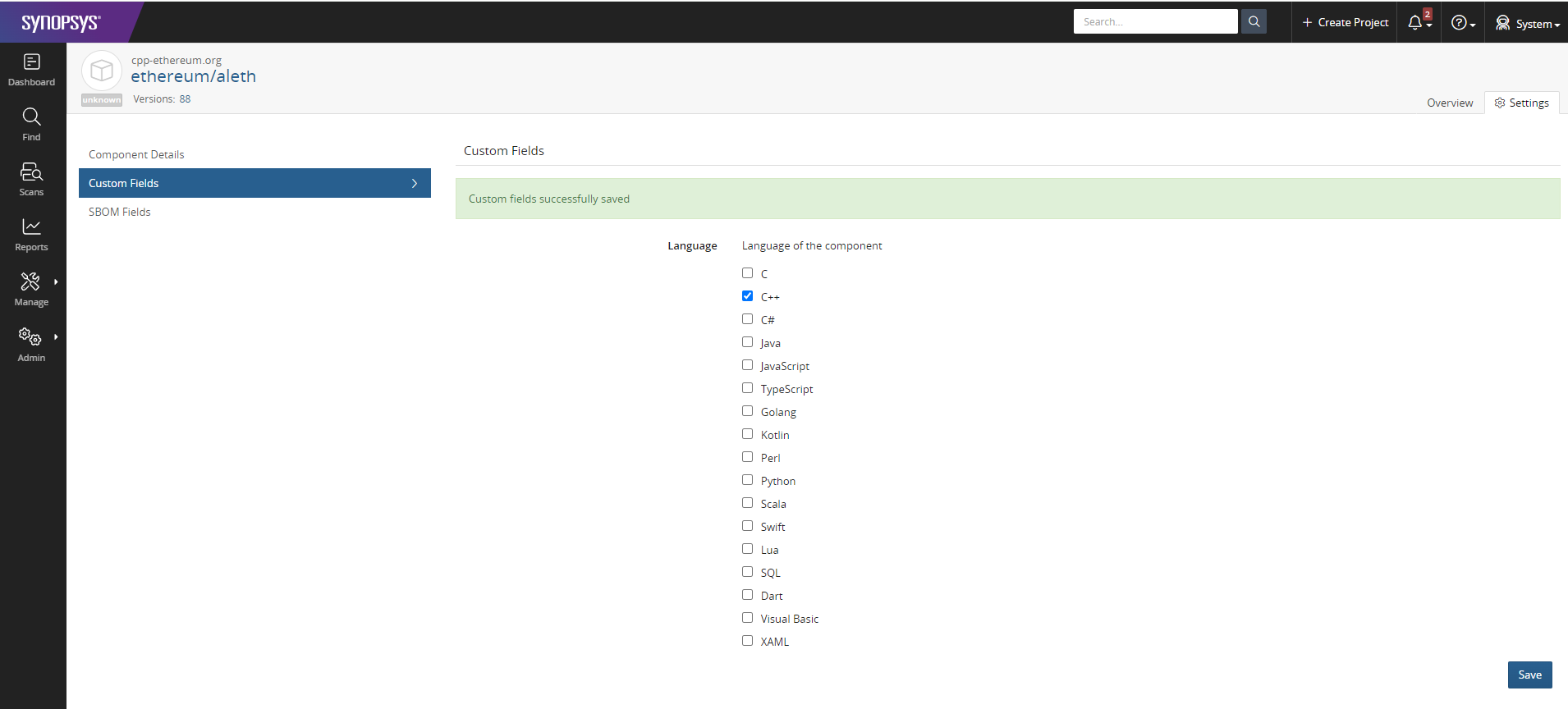
Then click on the Settings tab and go to menu Custom Fields. The Language custom field will appear with all its value options.
Check on applicable language(s) for the component. In the example below, we set the component "ethereum/aleth" to language "C++".
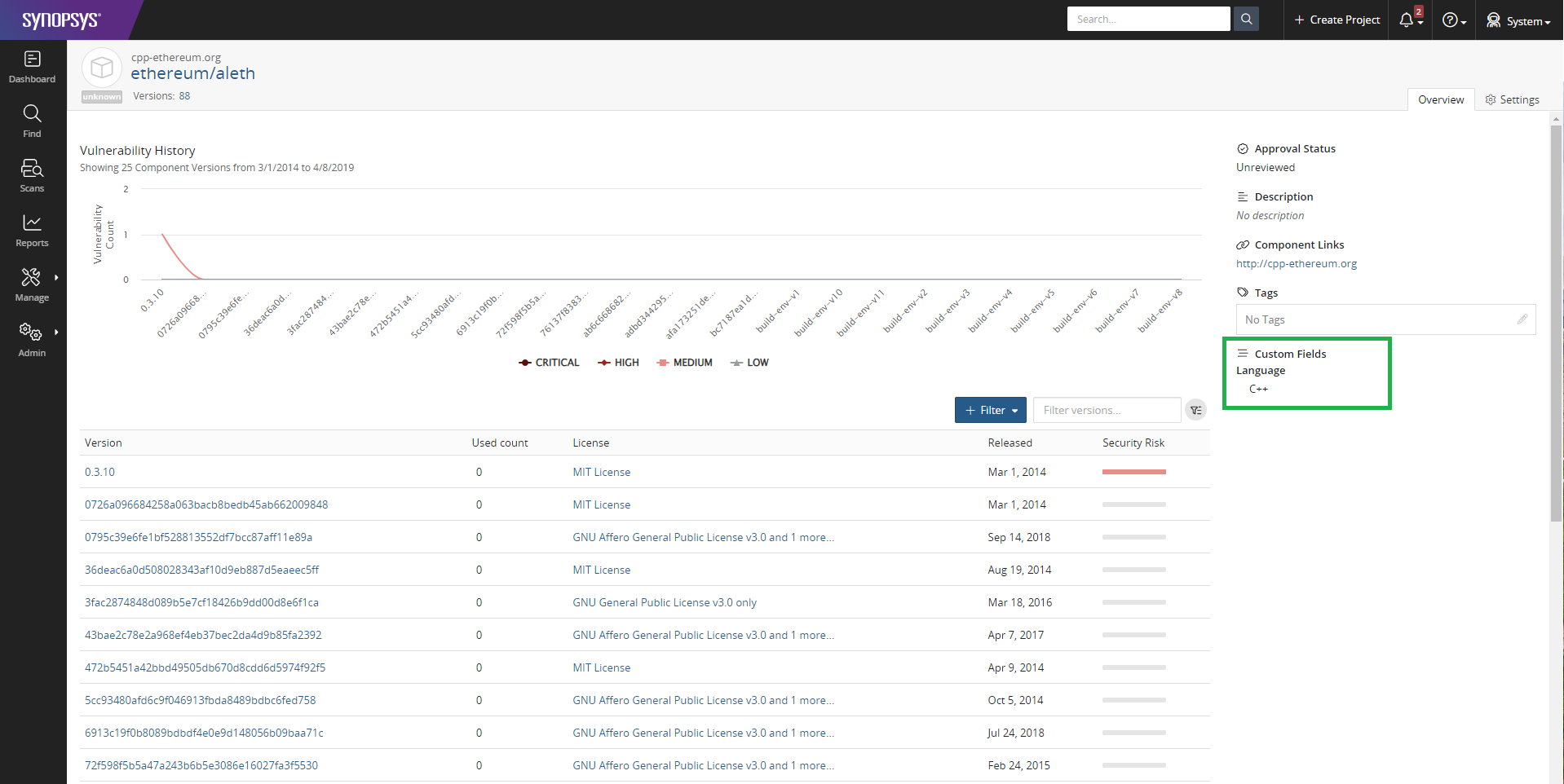
Viewing the Language custom field in a Black Duck dashboard
The Language custom field for component "ethereum/aleth" is now set to C++ and this can be seen in the component's page as shown below:
Black Duck Scope custom field
Black Duck is not really context aware, thus it is possible that some software is scanned unintentionally.Software developers prefer to have only Black Duck violations that are relevant to the files they are assigned to, so that the TICS results are actionable, and they are capable of resolving them. This means that the file scope should be taken in account. This can be done using the Scope custom field within Black Duck.
Creating the Scope custom field in a Black Duck dashboard
The Scope custom field is applied on a BOM component level. To create the custom field, from a Black Duck dashboard, go to menu Manage -> Custom -> BOM Component. Use field type "Text" for this custom field.
Fill out the relevant fields for the custom field as described below:
- Set the
Labelof the custom field to "Scope". - Set the
Descriptionof the custom field to "Component scope. This field can contain semicolon separated list of paths.".
Activate the Scope custom field by sliding the Active option slider for the custom field.
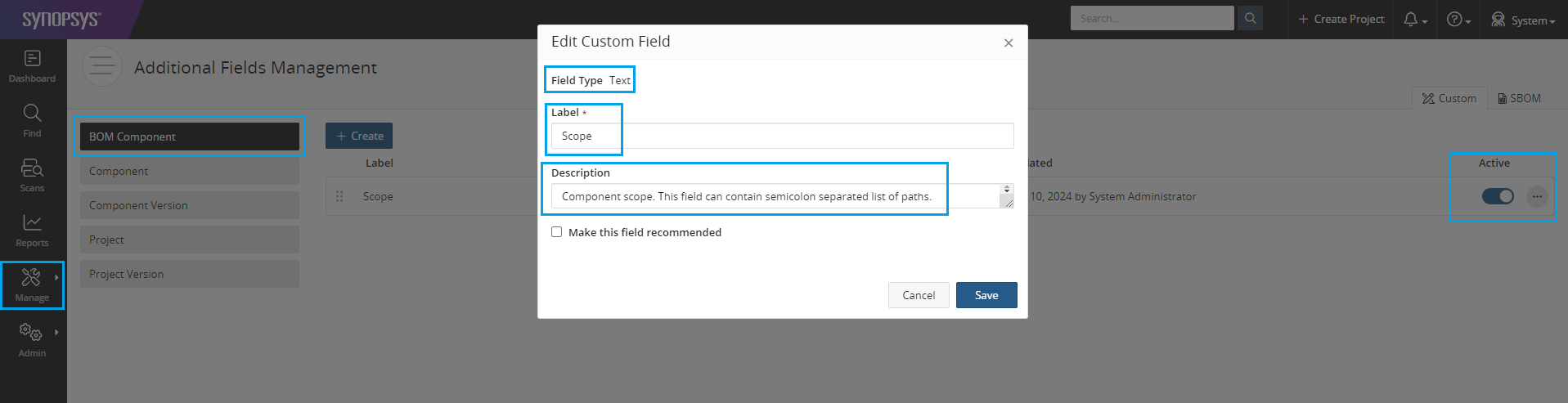
Setting the Scope custom field in a Black Duck dashboard
Now that we have created the Scope custom field, we can set a list folder or file paths where the component is used in the project. The path should be relative to the branch directory of a relevant TICS project.
- Open a BOM component list of a project version.
- Click on the
More option ...button on the right side of a component. - Click on menu "Custom Fields", the custom field Scope should appear.
- Fill out the desired folder or file paths separated by a semicolon in the text box.
- Click
Update
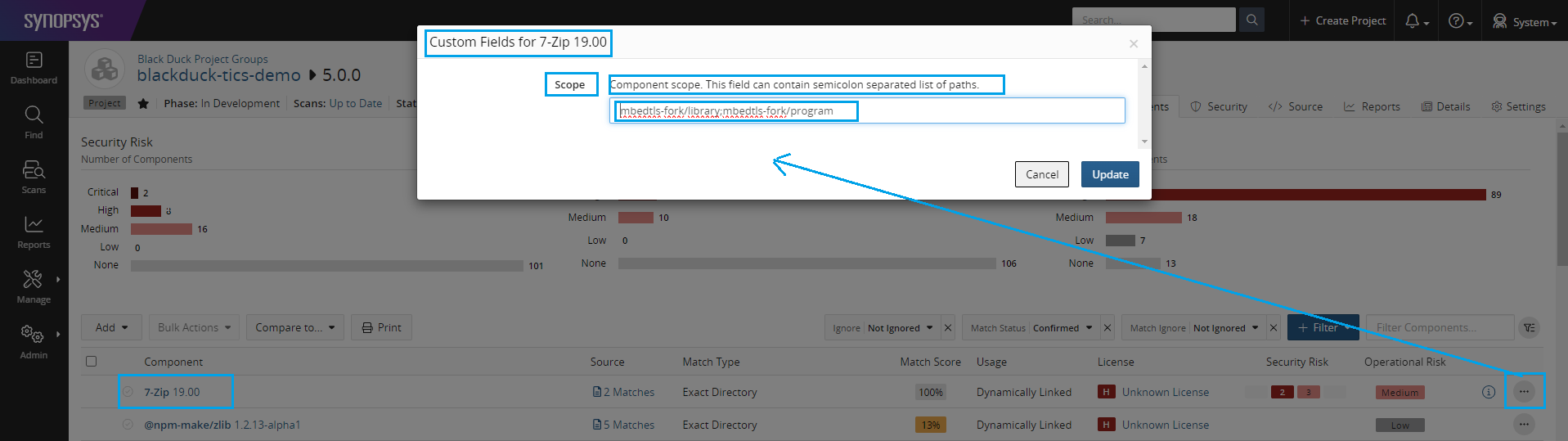
Viewing the Scope custom field in a Black Duck dashboard
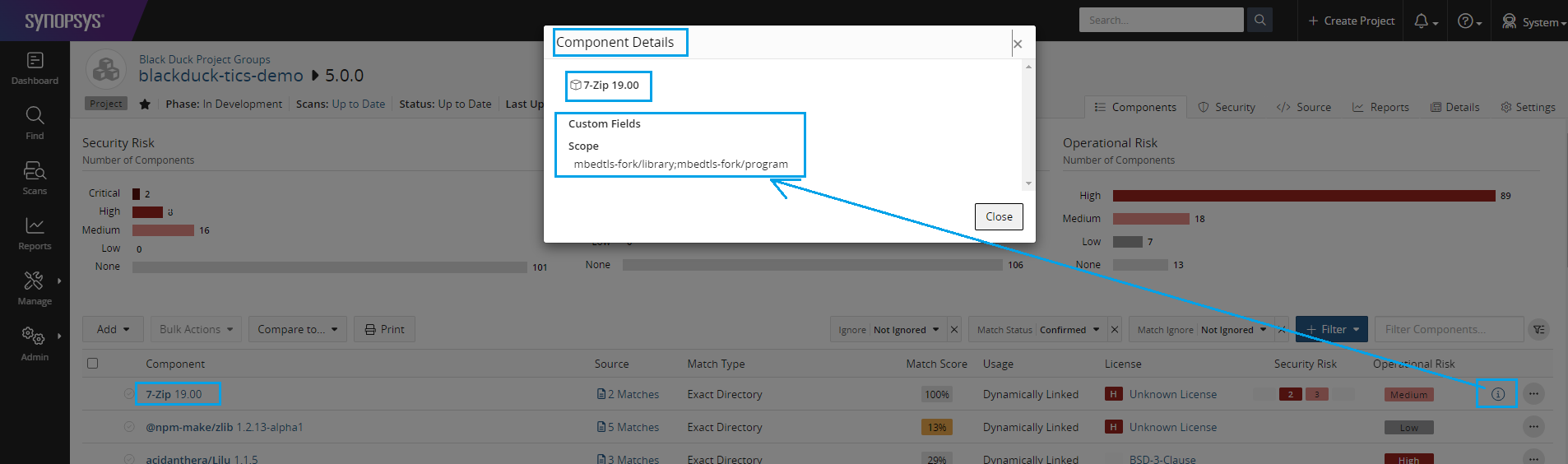
To view the Scope custom field value of a BOM component, go to a BOM component list of a project version. Click on the info (i) button.
The Scope custom field and its value is now shown.